Our earlier uncovered story explained the misconceptions or false narratives surrounding the 700 MHz band. We concluded in the story that other aspects would be discussed in a different report, so let’s look into one more aspect now. Another misconception or false narrative that is widely in circulation is about 5G NSA and 5G SA. So in this story, we tried to explain the same in Layman’s terms using examples that anyone can understand. Also Read: Advantage of Airtel 5G With Respect to Coverage and Experience Explained
High-level Architecture of 5G NSA and SA Deployment
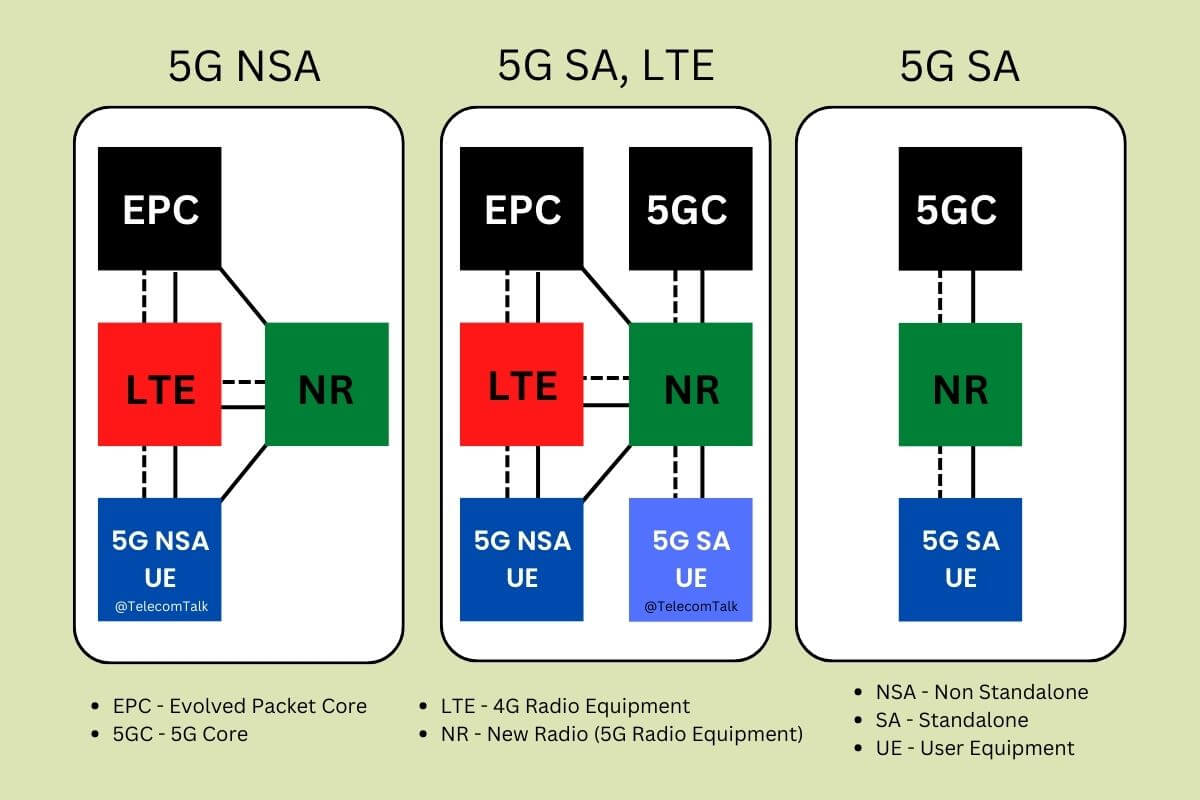
The image above gives a high-level overview of the 5G Non-Standalone and 5G Standalone Deployments. The high-level deployment setup comprises of Let’s discuss Radio, UE and Core in this order.
1. Radio
Radios are communication equipment that links the users’ devices to the Cellular Network wirelessly. The above deployment architectures use LTE for 4G and NR for 5G. If you observe in both NSA and SA, Radios need to be deployed. A phase which generally takes time for the telcos to rollout the services. So, Airtel needs to deploy 5G NR Radios just like in the case of 5G SA. Airtel already has LTE Radios deployed for its 4G Network and is currently deploying NR Radio, just like in the case of SA, to deliver 5G services. Hence, this aspect is the same for NSA and SA. Remember the benefit Airtel has to deploy fewer Radios due to the Spectrum Strategy followed by the telco.
2. User Equipment (UE)
Smartphones, Dongles, and Devices connected to the respective Network (4G, 5G) are represented by User Equipment (UE). Simply put, UE is any smartphone or device that connects to the Network. As a wide range of handsets supports NSA, Airtel can deliver 5G experience to millions of its users without leaving the majority to wait for an update or buy a supported handset. Considering its existing user base and market scenario, Airtel must take every of its customer along while safeguarding the investors’ interests and future-proofing Networks for the CAPEX involved. Also Read: Airtel 5G Plus Supports All Major Smartphones. To speak with numbers, Airtel 5G Plus supports 170 plus smartphone devices in the market. If we consider SA, the handset ecosystem needs to evolve, which is why fewer supported devices exist— not talking about devices that already support SA. So, the (User Equipment) UE section of the architecture has nothing to do with a telco. A Core reason why Jio is taking time to ensure support for a range of handsets. Now, the only thing left from the Architecture is the Core. So, if we are talking about 4G Networks, it is EPC (Evolved Packet Core), and if we are talking about 5G, it is 5G Core (5GC).
3. What is 5G Core (5GC)?
The 5G Core is like the heart and brain of the 5G Networks. The 5GC acts as an enabler for next-generation networks. The Core consists of a Data layer, Control plane and User plane. The Core is a Service Based Architecture (SBA) that drives, and implements the quality of service, enforces policy, Authentication, Signalling, Analytics, Gateway functions etc., and everything related to the networks and functionalities for 5G. In 5G, the core network has evolved as cloud-native and can run as a scalable setup in virtualized environments. 5GCore comprises multiple functions that run as individual microservices which can scale as per needs. These functions also deliver 5G SA functionalities like Network Slicing, Ultra High Speeds, low latency, Enhanced Security, Network Exposure functions etc. The full 5G system includes eMBB (enhanced Mobile Broadband), mMTC (massive Machine Type Communications), URLLC (Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communications) etc. 5G Core has advantages compared to advanced EPC for use cases that are not so widely used from a consumer perspective, such as VR, AR, IoT, Network Slicing and others. 5GC is capable of delivering high capacities due to the improved functionalities in the system. So, when a telco sees demand for a particular feature 5GC offers, it can switch to 5GC at any point in time however they want, as everything is already ready. Simply put, the 5GCore can run in the Cloud, such as private Cloud, Google Cloud, AWS or any cloud of choice by the telco. You can read one such a story from the below link. Also Read: Telefonica Partners Google and Ericsson to Move 5G Core to Cloud Yes, it is the same, and a telco with NSA can do this at any point in time whenever it thinks the use cases and Market are suitable for Business. So why not now? It depends on how a telco sees the Market Dynamics, Global headwinds, and Return on Investments and has nothing to do with its Network Capabilities.
Example:
As 5GCore is complex for a general user, the below layman’s example will help you understand, but not an exact technical as is comparison.
Let’s say your Latest Computer Hardware as New Radio (NR). Notepad 2022 is EPC. Notepad 2023 is 5GC.
There are features that the 2023 version delivers, such as faster access, security etc. So, whenever you see a need for such features, you will upgrade to Notepad 2023 via Cloud, and there you have it. Similarly with 5GC.
NSA vs SA
In both cases, the significant difference you can notice from an architectural perspective is 5GC (5G Core), and the rest remains the same except for some upgrades that are vendor specific. Now that things are obvious, it is up to the logical reasoning of an individual on how they look at NSA or SA.
Advantages of NSA compared with SA
The advantages of NSA are telco-dependent based on the existing spectrum holdings, which is different with every telco. This is where Airtel has a unique advantage regarding its spectrum holdings in the context.
- As seen from the Architecture above, in SA mode, 5G comes on top of the 4G Layer, and both act independently, which has two disadvantages in the current scenario. Devices: Lack of a well-developed device ecosystem for SA devices. Spectrum and Propagation: The 3300 MHz band, the workhorse layer that delivers 5G Speeds, has less propagation than the 2300 MHz band, impacting coverage in urban areas. As a result, 5G SA needs a Sub GHz layer (700 MHz) to work in tandem with the 3300 MHz band, but it should be noted that 700 MHz is for coverage and not a capacity band. At best, the 700 MHz band can deliver 4G like speeds around 8-10 Mbps, provide coverage indoors and in far-flung areas, and nothing more, which is not what a customer expects from 5G. But NSA deployed by Airtel has this advantage where the 3300 MHz band acts as a Downlink, delivering 5G throughputs and the mid-bands (1800/2100) - the 4G layer taking care of the uplinks, extending coverage in Urban areas.
- Airtel can leverage existing 4G infrastructure at no extra cost since the setup is ready and already available. Irrespective of customer handset compatibility, users can enjoy 4G or 5G.
- Airtel’s strong Mid-band spectrum holdings are a reason for this unique advantage of 5G NSA. As the competition does not have enough mid-band spectrum, there is no choice apart from the 700 MHz band. So this results in a requirement for large-scale SA deployments and Radios, which require heavy CAPEX. A core reason why Jio’s Radios are more in number compared to Airtel’s as recently reported by Ministry of Communications. Airtel is currently installing an average of two radio transceivers on every tower to expand 5G coverage, while Reliance Jio is installing up to six as per a Business Standard Report.
- The NSA advantage is around experience, where Airtel users can enjoy a faster call connect time on Voice. In addition, it allows a faster uplink than anyone else, as Airtel holds a massive mid-band spectrum. You can check Airtel Spectrum Holdings from the page here: India Spectrum Holding Timeline
Deployment Options
There are multiple deployment options for Communication Service Providers (CSPs), as not everyone starts from the same point. For example, a new telco may start from scratch, some want a hybrid model (utilizing existing infrastructure), and some telcos wait for Market Dynamics and ROI. So, it all depends on the optimum utilization of resources while getting investment returns and future-proofing networks. So, 5G NSA and SA coexist for certain years, and 5G SA alone (case 3 from image) cannot exist as every telco has obligations to support roaming, a wide range of handsets etc. Moreover, various Network Vendors have multiple options and modules for deployment based on the proprietary tech they have developed as per 3GPP specifications. So, the above-discussed scenarios may have slight differences based on vendor or telco.
Conclusion:
Nowhere in the world can we see such a situation as in India. 3GPP consortium developed 5G NSA and SA specifications to ensure a smooth transition to Next Generation Networks. They must have never expected this would create circumstances for driving false narratives of exclusive benefits or capabilities for any specific telco. Ultimately, it depends on a particular telco, business decisions, market of operation and how a telco wants to evolve. Now that you know the difference between 5G NSA and SA, we will discuss other aspects in a different story.